ASTM F2622
OXYGEN TRANSMISSION RATE (OTR) WITH A GENERIC SENSOR
Standard Test Method for Oxygen Gas Transmission Rate Through Plastic Film
and Sheeting Using Various Sensors
Where Used
Evaluate materials for their permeability characteristics to oxygen gas. The method is used to optimize a product’s shelf life or use life and helps with choosing the most appropriate materials.
Description
This test method analyzes the amount of oxygen (at steady state) that is permeating through a flat film (such as the sidewall of a pouch).
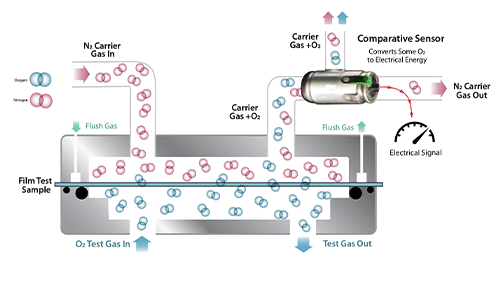
- One side of the sample is challenged by oxygen gas (typically at 100% or room air at 20.9%), while the other side of the sample is swept by a nitrogen carrier gas.
- The transmitting oxygen gas is swept by the nitrogen gas through the sensor, where a portion of the gas stream is analyzed to determine the amount of oxygen gas permeating through the sample.
- Because only a fraction of the permeating oxygen is consumed with these sensors, generic oxygen sensors require calibration and routine verification with reference materials to ensure accuracy of results.
- Common units for OTR are cc/(m2 • day) or cc/(100in2 • day).
- For more details on ASTM F2622 please visit the ASTM website.
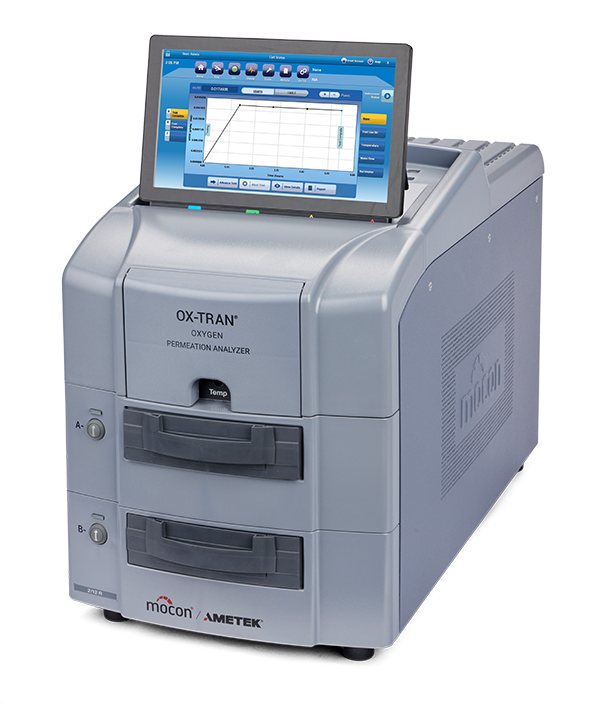
Method Schematic and Related Instrument

Note
This test method is often used with high transmission rate materials (greater than 1 cc/(m2 • day)) as it lacks the sensitivity found with the coulometric detector utilized with ASTM D3985 and ASTM F1927. This standard was developed to allow for the use of various oxygen sensors and works well for materials utilized with produce packaging, silicone rubbers and coated papers. Learn more about our Lab Testing Services here.
Results
The transmission rate output is a graph of OTR vs time (which is key to verifying equilibrium) and data report. Transmission rate test duration can range from a few hours to a few days, as this method is most often used with faster, higher transmitting materials. Additionally, moisture-sensitive samples (e.g. coated paper) have OTRs that are impacted by humidity and this methodology can incorporate humidity control. Knowing your product’s needs and storage conditions is important for optimizing the appropriate test environment.
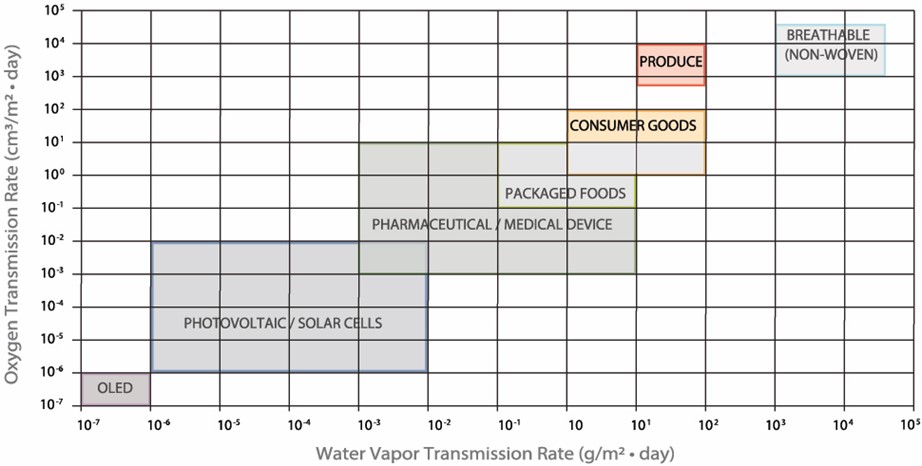
Below are example applications where this methodology can be appropriate.
Download the ASTM F2622 Note